RESULTS
The main objective of the project was building a cluster/grid calculation platform, in order to use it in molecular modelling and modelling on the meso and macroscopic level of complex materials. The project was coordinated by the Babes-Bolyai University, in a partnership with the Technical University in Cluj Napoca. This platform represents to this day the most powerful IBM calculation node in the country.
The node facilitates the running of molecular modelling calculations on any given chemical and biochemical systems with up to thousands of atoms (also depending on the chosen method of investigation), but also on complex materials in order to determine their various properties/characteristics.
The first stage of the project had as an objective the aquisition procedures, taking into account the value of the equipment and the drafting of the auctioning papers. The technical characteristics were formulated for each piece of equipment with a view to a technical and legally correct drafting of the technical specifications for the aquisition.
The second stage (2008) consisted of activities related to the design of the space and the equipment acquisition. The procedures were started at the beginning of 2008, so that the deadline for this stage can be observed.
Following the auction launched during May and finalised in July, IBM equipment was purchased in order to build the “Molecular Modelling and Computational Quantum Chemistry Centre”- Calculation node complete solution.
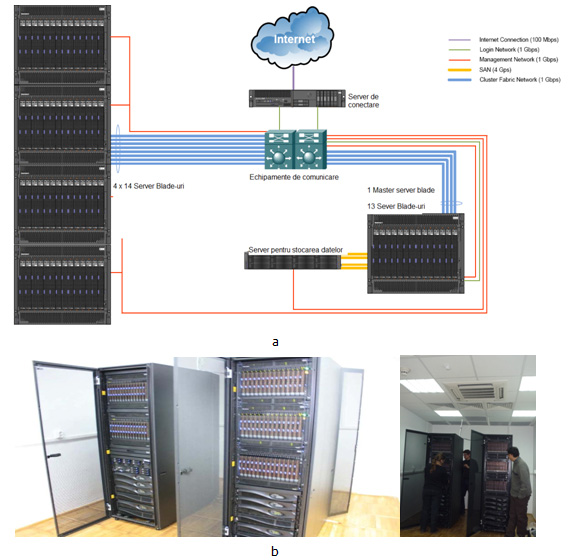
Figure 1. Frontal view of the node
Ten remote connection points have been set up, both within the premises of BUU and those of the Technical University. The connection points in UBB and the connection node in UTC-N were equipped according to specific activities.
In the third stage (2009), the configuration of the acquired equipment in order to set up the grid cluster was scheduled.
A Linux (Red Hat 5.3) operating system was installed and the grid cluster structure, sen as the most recent and complete evolution of distributed processing, was configured. This configuration allows for the optimization of calculation processes by executing several tasks on several machines, conceived as a unique computer and for the flexible, certain and coordinated division of resources among dynamic teams of individuals or institutions.
The administration system resulted allows for real time monitoring of the users activities and for the managing the extent to which the resources are used. The visualization of these functions is achieved by means of the Ganglia program, which was especially conceived for platforms functioning as clusters or grids.
The specific calculations programs presently installed on the platform are Gamess(USA), NWchem, SCC-Dftb+ Mopac, ORCA, Cfour, NBO, etc. Gaussian 09 and ADF-2009 are currently to be acquired and to be tested for parallel running.
At this stage, tests have been run on chemical systems relevant for our current research projects.
For example, methanol-benzene interactions, as well as the electronic and structural properties of these systems have been investigating using the MPWB1K and M06-2X functionals with the 6-31+G** basis set. It has been noticed that the M06-2X functionals give similar results to the somewhat more expensive perturbational method MP2(fc). The investigations carried on led to the conclusion that the preferred structure (with H-pi interactions between the proton on the methylenic OH group and the pi electronic system of the benzene) is determined not by the minimum of the total energy, but by the free energy minimum, the contribution of entropic effects bearing a decisive influence on the preference for a certain configuration.
The available resources were also used to run molecular modeling calculations in the case of another research program, Capacitati Modul III 32/01.06.08, The study of kinetically controlled conformations for sensitive and selective host molecules with applications in farmacy and food chemistry.
Calixarenes were investigated as host molecules in the transport of ions and neutral molecules. The size of the molecules studied (a non functionalized calix[4]arene with the formula C28H24O4 has 56 atoms) considerably limits the choice of method and basis sets used, involving a large amount of time if the calculations are run on a regular computing system. Thus, the use of larger computational resources is essential. Within this project,. A first step involved the optimization of several calix[4][5][6][8]arene geometries, functionalized on both the upper and lower rim, in order to evaluate the effect of the substituents on the cavity size and flexibility. In a second stage, an indolic derivative was inserted in the calixarene basket. Geometry optimization calculations, frequency and NBO analysis, salvation calculations were run and the host-guest interaction energy was determined.
As a conclusion, the project Molecular Modelling and Computational Quantum Chemistry Centre was materialized in an state of the art, grid/cluster calculation platform, which allows the access to one of the most modern calculation techniques. The operating systems are secure and user friendly. All interested researchers in the field of Chemistry, Physics, Mathematics, Materials Science and Engineering, etc. can benefit from the use of this laboratory. The node will be extensively used for the MA classes in Molecular Modelling in Chemistry and Biochemistry offered by the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering.